Duration is the term used to describe how the value of a fixed income security, such as a bond or loan, is likely to change when official interest rates move.
Investors use duration as a way of measuring interest rate risk. A change in interest rates can impact the price of the security at any time prior to maturity. When investing in fixed income, the duration of the investment is an important factor to consider given the potential implications to the investor. This includes the potential for a change in interest rates to have a negative impact on investment returns.
Both maturity and duration are measured in years, however they mean very different things. Maturity simply refers to the amount of years until the principal amount of a debt instrument (for example, a bond) is repaid. If interest rates move, the maturity of a bond doesn’t change. On the other hand, duration refers to the sensitivity of a bond’s price to changes in interest rates. The longer the duration, the more the value of the loan will vary with interest rates. If investors believe that interest rates will rise, they may seek to find fixed income securities that have low duration. This would include securities with a short maturity and aim to also reduce interest rate volatility. Conversely, if interest rates fall then the price of the fixed income security will increase. Therefore, investors who want to benefit from a fall in interest rates may look towards securities with long duration.
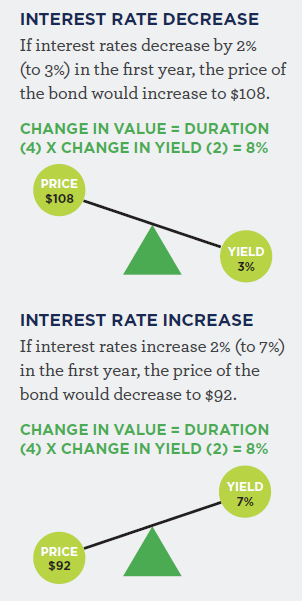
The example to the right demonstrates how duration affects the price of a bond when there is a change in interest rates .
Assume a $100 face value with an interest rate of 5% p.a. and a duration of 4 years.
As shown in the example, as interest rates decrease, the price of the bond increases. Whereas when interest rates increase, the price of the bond falls.